It’s PTSD: The Road to Recovery For Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition that can affect people who have experienced or witnessed a traumatic event. It can cause a range of symptoms, including flashbacks, nightmares, anxiety, and depression, which can have a significant impact on a person’s daily life. PTSD is often associated with military combat, but it can also affect survivors of sexual assault, domestic violence, natural disasters, and other traumatic events.
Living with PTSD can be challenging, but there are treatments available that can help individuals recover and lead fulfilling lives. Seeking treatment for PTSD is an essential step towards recovery, but many people may not realize they have the condition or may be hesitant to seek help due to stigma or a lack of understanding about the disorder.
In this article, we will explore what PTSD is, the signs and symptoms to look out for, and the road to recovery for those living with the condition. We will also discuss the importance of seeking professional help, and provide resources and support for those who may be struggling with PTSD.
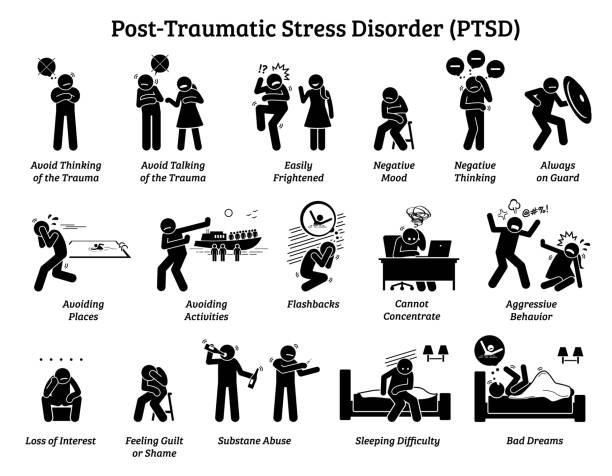
Symptoms of PTSD
Symptoms of PTSD can vary widely and can be different for each person. However, there are some common symptoms that many people with PTSD experience. These symptoms are typically grouped into four categories: re-experiencing, avoidance, negative changes in mood and cognition, and hyperarousal.
Re-experiencing symptoms may include flashbacks, nightmares, and intrusive thoughts or memories of the traumatic event. These symptoms can be triggered by things that remind the person of the trauma, such as certain smells, sounds, or sights.
Avoidance symptoms may include avoiding situations or people that remind the person of the trauma, or feeling emotionally numb or detached from others. The person may also have difficulty remembering important details about the traumatic event.
Negative changes in mood and cognition symptoms may include feelings of guilt, shame, or hopelessness. The person may also have a negative view of themselves or the world around them, and may have difficulty experiencing positive emotions.
Hyperarousal symptoms may include feeling constantly on edge, irritable, or easily startled. The person may also have difficulty sleeping or concentrating, and may engage in impulsive or self-destructive behavior.
It is important to recognize these symptoms and seek help if they persist or interfere with daily life. While some people may experience symptoms immediately following a traumatic event, others may not develop symptoms until months or even years later. If left untreated, symptoms of PTSD can worsen over time and lead to other mental health conditions.
It is also important to note that symptoms of PTSD can vary in intensity and duration. While some people may experience severe symptoms, others may have mild symptoms that are easily managed with appropriate treatment. It is essential to understand that each person’s experience with PTSD is unique, and there is no “right” or “wrong” way to feel or react to a traumatic event.
Recognizing symptoms and seeking help from a mental health professional can make a significant difference in managing and recovering from PTSD. A mental health professional can provide a proper diagnosis, develop an effective treatment plan, and offer support and guidance throughout the recovery process.
Causes of PTSD
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) can develop after someone has experienced or witnessed a traumatic event that caused intense fear, helplessness, or horror. The symptoms of PTSD can cause significant distress and affect different areas of life, including work, school, and relationships.
While anyone can develop PTSD, certain factors can increase the risk. For example, people who have experienced repeated traumatic events or have a family history of PTSD may be more likely to develop the condition. Additionally, PTSD can occur at any age, and women are more likely to develop PTSD than men.
There are many different types of traumatic events that can cause PTSD. Some common examples include military combat, physical or sexual assault, natural disasters, accidents, or the sudden death of a loved one. People who have experienced chronic or ongoing trauma, such as childhood abuse or neglect, may also develop PTSD.
It’s important to note that not everyone who experiences a traumatic event will develop PTSD. Research suggests that factors such as resilience, social support, and coping skills can help protect against the development of PTSD. Additionally, the severity and duration of the traumatic event can play a role in the likelihood of developing PTSD.
Recognizing the potential causes and risk factors for PTSD is an important step in understanding and managing the condition. By identifying the factors that may have contributed to the development of PTSD, individuals can seek appropriate treatment and support to address their symptoms and work towards recovery.
Treatment options for PTSD
PTSD is a treatable condition, and there are several options available for people suffering from it. The most effective way to treat PTSD is through a combination of therapy and medication.
Therapy is considered the primary treatment for PTSD. Different types of therapy may be effective for PTSD, including cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR), and Prolonged Exposure (PE) therapy. CBT involves identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to PTSD symptoms. EMDR is a type of therapy that uses eye movements to help people process traumatic memories. PE therapy is a type of therapy that helps individuals confront their trauma through gradual exposure to the memories that are causing their PTSD symptoms.
Medication may also be used in conjunction with therapy to treat PTSD. Antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), can be helpful in reducing symptoms of depression, anxiety, and other mood disorders associated with PTSD.
It is important to seek treatment for PTSD as soon as possible after experiencing symptoms. The longer symptoms go untreated, the more difficult they can be to treat. Treatment can significantly reduce the severity of symptoms and improve quality of life.
It is also important to note that not all treatments work for everyone, and it may take some time to find the right combination of therapies and medications that work for an individual. However, research has shown that treatment for PTSD can be effective in reducing symptoms and improving overall well-being.
In addition to therapy and medication, lifestyle changes, such as exercise, meditation, and healthy eating habits, may also help manage symptoms of PTSD. Support from loved ones, friends, and community resources can also be helpful in the recovery process.
Overall, it is essential to seek treatment for PTSD, as it can significantly impact one’s quality of life. There are many effective treatment options available, and with the right combination of therapies and support, individuals with PTSD can recover and lead fulfilling lives.
The road to recovery
The journey to recovery from post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is not an easy one, but it is certainly possible. Recovery from PTSD involves learning how to manage symptoms and work through the traumatic event(s) that caused the disorder. In this section, we will discuss the road to recovery for PTSD.
Explanation of the journey to recovery: Recovery from PTSD is a process that involves different stages and varies from person to person. It can take time and patience to overcome the symptoms of PTSD, and it’s important to remember that recovery is a journey, not a destination. The first step towards recovery is acknowledging the presence of PTSD symptoms and seeking help.
The journey to recovery may involve different types of therapy and other treatment options. Psychotherapy, also known as talk therapy, is often used to treat PTSD. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), exposure therapy, and eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) are some of the common types of therapy used for PTSD treatment.
In some cases, medication may be prescribed to manage symptoms such as anxiety, depression, and insomnia. However, medication should not be the only treatment option as it does not address the root cause of the disorder.
The importance of a support system: Having a support system is crucial in the recovery process for PTSD. Family, friends, and other loved ones can provide emotional support and help the person with PTSD feel less isolated. Support groups and group therapy sessions can also be beneficial for individuals with PTSD as they can connect with others who have experienced similar traumas.
It’s important to note that building a support system takes time, and not everyone will have a supportive network. In such cases, seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor can provide the necessary support needed for recovery.
How to support someone with PTSD: Supporting someone with PTSD can be challenging, but it is essential for their recovery. Here are some tips on how to support someone with PTSD:
- Listen without judgment: It’s important to listen to the person with PTSD without judging them. Allow them to express their feelings and emotions in a safe and non-judgmental environment.
- Encourage treatment: Encourage the person with PTSD to seek professional help from a therapist or counselor. Offer to help them find a therapist or accompany them to appointments.
- Be patient: Recovery from PTSD takes time, and it’s important to be patient with the person with PTSD. Avoid putting pressure on them to “just get over it” or “move on.”
- Educate yourself: Educate yourself on PTSD and its symptoms. Understanding the disorder can help you be more supportive and empathetic towards the person with PTSD.
Essentially, the recovery from PTSD is possible, but it takes time and effort. Seeking help, building a support system, and being patient are essential in the road to recovery. Supporting someone with PTSD can also be challenging, but with the right approach, you can make a significant difference in their recovery journey.
Conclusion
In conclusion, PTSD is a severe mental health disorder that can significantly impact an individual’s daily life. It is important to recognize the symptoms of PTSD and seek treatment as soon as possible to prevent the condition from worsening. Various treatment options are available, including therapy and medication, and seeking treatment is critical for recovery.
The road to recovery for PTSD can be challenging, but it is a journey that can be successful with proper treatment and a strong support system. It is essential to have a support system of family and friends who understand the condition and can provide emotional support throughout the recovery process.
For those supporting someone with PTSD, it is important to be patient and understanding. It is important to listen without judgment and encourage them to seek professional help. Encouraging healthy coping mechanisms such as exercise, mindfulness, and relaxation techniques can also be helpful.
To sum it up, PTSD is a complex condition that requires proper diagnosis and treatment. With the right support and treatment, individuals with PTSD can manage their symptoms and work towards recovery. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of PTSD, it is crucial to seek help from a qualified healthcare professional. Remember, there is no shame in seeking help, and recovery is possible.
Here are some reputable organizations that provide resources and support for individuals with PTSD:
- National Center for PTSD: https://www.ptsd.va.gov/
- American Psychological Association: https://www.apa.org/topics/trauma-ptsd
- Anxiety and Depression Association of America: https://adaa.org/understanding-anxiety/posttraumatic-stress-disorder-ptsd
- National Institute of Mental Health: https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/post-traumatic-stress-disorder-ptsd/index.shtml
- Sidran Institute: https://www.sidran.org/resources/for-survivors-and-loved-ones/post-traumatic-stress-disorder/
- PTSD Alliance: https://www.ptsdalliance.org/
- Wounded Warrior Project: https://www.woundedwarriorproject.org/mental-health/conditions/ptsd
- Make the Connection (U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs): https://maketheconnection.net/conditions/ptsd
It is important to note that seeking help from a mental health professional is crucial in the treatment of PTSD. These organizations can provide helpful resources and information, but they are not a substitute for professional treatment.








